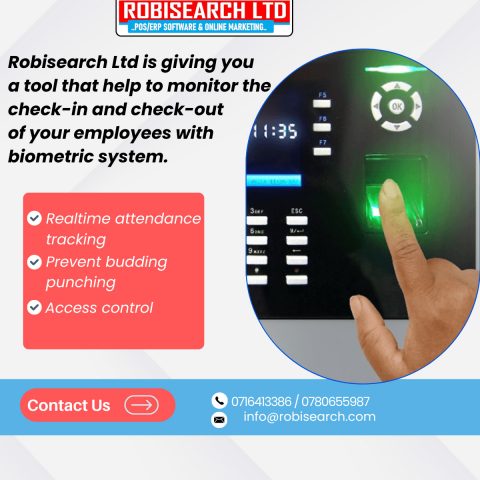
Biometric systems—using fingerprints, faces, or even irises—are now common in modern workplaces for security and time tracking. They replace old key cards and password logins, offering a faster and far more secure solution.
But how does placing your finger on a sensor actually verify who you are?
It’s not magic; it’s a quick, two-phase process that turns your unique physical traits into a secure, digital identity. see what a biometric system entails https://youtube.com/shorts/JD9yLZ-NQXs?si=qUoGRVTF3qLq8qXw

face and finger print biometric
Phase 1: Enrollment (The One-Time Setup)
This is the initial step where you register yourself with the system.
Step 1: The Scan (Data Capture)
You interact with the device for the first time. You might place your finger on the sensor, or look at the facial recognition camera. The device captures a raw, digital image of your unique feature.
Step 2: Template Creation (The Secure Code)
The system instantly measures the unique characteristics of that image (like the distance between points on your face or the points where your fingerprint ridges end). It then converts these measurements into a unique, encrypted mathematical code called a template.
Crucial Detail: The system never stores the raw picture of your face or finger. It only stores this non-reversible, secure mathematical code.
best for offices and schools
Step 3: Secure Storage
This encrypted template is stored on the central server, linked to your employee ID. This code is the baseline the system will use for all future comparisons.
Phase 2: Verification (The Daily Clock-In/Access)
This is the quick process that happens every time you clock in for work or try to enter a restricted area.
Step 4: Live Scan
When you arrive, you interact with the scanner again (e.g., placing your finger or looking at the camera). The device captures a fresh, live scan.
Step 5: Real-Time Comparison
The system immediately converts this new live scan into a temporary mathematical code. It then compares this new code to the original, securely stored template (from Step 3).
Step 6: Access Granted or Denied
If the two codes match within a high degree of similarity, the system verifies your identity and takes the programmed action:
-
Time Tracking: It logs your accurate clock-in time.
-
Access Control: It unlocks the door or barrier.
If there is no match, access is denied, protecting the workplace against unauthorized entry and “buddy punching” (where one employee clocks in for another). visit our website https://robisearch.com/biometric-time-attendance/

increase employee productivity
3 Must-Know Biometric Features
A good workplace system must have these features to be effective:
-
Speed: Verification must be nearly instant (under one second) to prevent lines and slowdowns.
-
Anti-Spoofing: The system must check for liveness (e.g., body heat or subtle movement) to prevent fraud using photos, molds, or other non-live objects.
-
Data Safety: The use of mathematical templates (instead of images) ensures that even if the system is compromised, the sensitive biometric data cannot be stolen or misused. click to understand more https://youtu.be/RmLYjQztSoE?si=oJNiFdjzBQjOlFFM
the best biometric system
Conclusion
The power of the workplace biometric system lies in its simplicity and security. By quickly converting unique human traits into irreversible mathematical codes, these systems eliminate the common flaws of keys, cards, and passwords. They deliver instant verification, eliminate fraud like “buddy punching,” and provide an accurate, tamper-proof audit log for all access and time tracking. The result is a workplace that is safer, more efficient, and fully prepared for the digital future.
Stop relying on easily compromised passwords and key cards. Implement a modern biometric solution to guarantee accurate time logs, eliminate buddy punching, and ensure only authorized personnel gain entry.
call/whatsapp +254716413386 +254780655987
email robisearch@gmail.com
to get qoutation https://robisearch.com/quotation/

